Maternity Benefits in Bangladesh
Women, performing manual and physical labour other than intellectual, administrative, supervisory or managerial in Bangladesh are entitled to 16 weeks of Paid Maternity Leave – eight weeks before birth and eight weeks after birth. The terms and conditions of employment, including the Maternity Benefits of the female staff performing intellectual, administrative, supervisory or managerial positions should be regulated in the employment contract. No paid maternity leave shall be granted to women, who at the time of her confinement has two or more surviving children. In that case she shall be entitled to the leave, which she otherwise be entitled to.
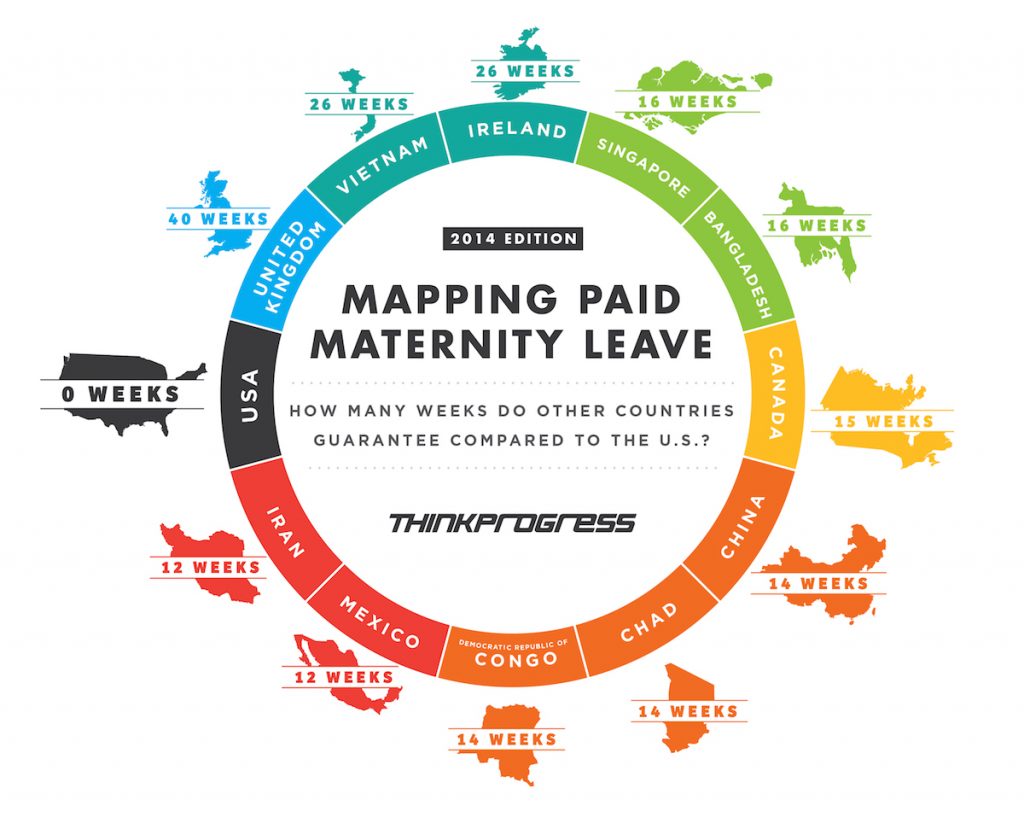
In the latter half of the 20th century, there has been a dramatic rise in the proportion of women who have entered the workforce throughout the world. In Bangladesh the number of working women has also gone up in the last decades. As per available data of Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS) in 2006, of the 49.5 million of civilian workforce, about 38% are female (BBS, 2006). With the increasing number of working women worldwide the paid Maternity Leave has become more relevant than ever before in history.
Evolution of Maternity Benefits in Bangladesh
The centuries old labour law system in Bangladesh was enacted during the British rule of the Indian sub-continent, in 1881. Later, laws governing different employment and labour related matters, e.g., The Factories Act (1881), Workmen’s Compensation Act (1923), Trade Unions Act (1926), Trade Disputes Act (1929), Payment of Wages Act (1936), Maternity Benefits Act (1939), and the Employment of Children Act (1938) were a few of the employment and labour laws enacted during that period. After independence of the Indian sub-continent, including Bangladesh, in 1947, almost all the laws during the pre-partition period remained in force with some modifications and amendments in the form of administrative rules, by the then Pakistan (Bangladesh was called East Pakistan at the time) Government.

After the independence from Pakistan in 1971, the Bangladesh government retained the previous laws through the Bangladesh Laws Order (President’s Order No. 48). No major development took place in the history of labour legislation till the enactment of the Bangladesh Labour Act 2006. The Bangladesh Labour Act 2006, amended on the 14th November 2018, is a major and comprehensive enactment regarding industrial relation system through codification of existing labour laws in order to avoid overlapping and inconsistencies and brought some significant changes in industrial relation systems.
Before the amalgamation of all the labour laws through the Bangladesh Labour Act 2006, there were three distinct acts for the regulation of Maternity Benefits for women for certain periods before and after child birth and for the payment of maternity benefits to them. These were The Maternity Benefits Act 1939 (which was most widely used in manufacturing, service and other organisations), The Mines Maternity Benefit Act 1941, and The Maternity Benefits (Tea Estate) Act 1950. All three of these acts have been repealed and amalgamated into the new labour laws under Chapter IV as “Maternity Benefits”.